Using a solution-focused approach for goal achievement: peer coaching
Problem-focused’ and ‘solution-focused’ are two different approaches that can be used to address challenges or issues.
- Problem-focused approaches involve identifying and analysing the problem itself – its causes, consequences, and possible solutions. Problem-focused strategies often involve breaking down the problem into manageable chunks, gathering relevant information, and developing action plans to address it systematically.
- Solution-focused approaches emphasise identifying and drawing upon existing strengths and resources to find solutions. Rather than dwelling extensively on the problem itself, solution-focused strategies focus on envisioning the desired outcome and identifying steps to achieve it. This often involves exploring exceptions to the problem, identifying past successes in managing such difficulties, and building on existing strengths to create change.
Reflective pause:
How do you balance problem-focused and solution-focused approaches to effectively cope with challenges?
Studies show that health and social care practitioners find support from peers particularly helpful when coping with challenges (Chang, 2018). Peer coaching is a solution-focused approach where peers support each other to achieve their goals through positive, forward-looking conversations. Setting up a peer-coaching initiative can help you find solutions to a problems you are stuck with.
All you need is a willing colleague who also wants to benefit from this approach. Instead of dwelling on problems or obstacles, peer coaches encourage the coachee (the person being coached) to envision their ideal future, explore what is already working well, and identify small, achievable steps to move forward. By emphasising empowerment, collaboration, and self-discovery, solution-focused peer coaching fosters a supportive and growth-oriented environment for individuals to maximise their potential and achieve meaningful progress.
Peer coaching aims to:
- Provide a structured approach to helping.
- Enable someone to generate specific, measurable goals that are realistic but stretching.
- Help them identify ways to achieve those goals.
- Provide objective, non-evaluative feedback about how they are progressing towards achieving their goals.
- Offer support and encouragement when they need it.
How does peer coaching work?
- Peer coaching is a relationship where two colleagues take it in turns to be the coach and the ‘coachee’ (i.e. the person being coached).
- It draws on intrinsic values and beliefs.
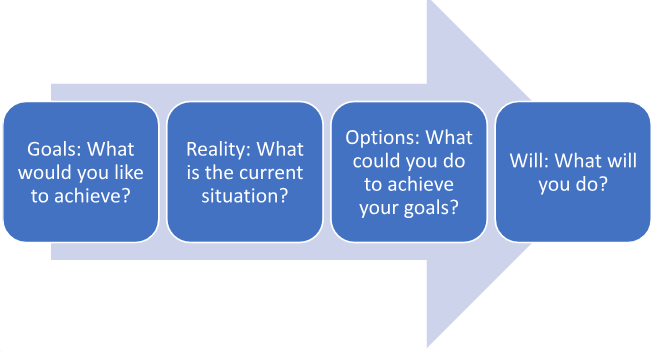
- It uses the GROW model as a framework:
- The coachee identifies the GOAL they wish to achieve.
- The coach helps them reflect on how REALISTIC the goal is, based on their commitments and the time and resources available.
- Both parties work together to help the coachee generate a range of creative OPTIONS for meeting the goal.
- The coachee develops the WILL to meet the goal by making an action plan and a commitment to making changes or taking action.
There are some practical considerations to consider when setting up a peer coaching relationship:
- Peer coaching can be conducted face to face, online, or by phone. Regular and formal contact (by any of these methods) is essential to ensure the coachee maintains focus on their goals.
- Trust between partners is essential as the process requires self-disclosure.
- Partners should be well matched in their working styles and expectations of the coaching relationship.
- Peer coaching can be conducted face to face, online, or by phone. Regular and formal contact (by any of these methods) is essential to ensure the coachee maintains focus on their goals.
- Venting is important, but the coach should help the coachee move beyond emotional release towards finding constructive solutions.
- The coach needs to keep the conversation on track, as it is easy to drift.
- Active listening and open/probing questions are required.
Peer coaching offers important benefits such as improved goal setting, stress management skills, wellbeing and job satisfaction (Gyllensten & Palmer, 2006). It also helps protect mental health during stressful periods (Short et al., 2020). Being a peer coach can help health and social care professionals develop essential interpersonal skills such as active listening, building rapport and trust, enhancing empathy, and promoting reflection and awareness. These skills are invaluable for strengthening relationships between practitioners and people who access services.
Guidance on how to move from focusing only on problems to focusing on solutions in peer coaching is set out below.
Moving from a problem-focus to a solution-focus in peer coaching
- Being problem-focused
Use the questions below to talk (for about five minutes) about a recent situation that has caused you difficulty. Person A (the coachee) describes the situation. Person B (the coach) directs the conversation with the following questions.
- ‘So, what is the problem?’
- ‘What happened?’
- ‘What do you think is the cause of the problem?
- ‘Who is to blame?’
- ‘What have you tried in order to fix it?’
- ‘Why is this still a problem?’
- ‘How can you stop this happening again?’
2. Being solution-focused
The coach should spend about five minutes supporting the coachee to discuss a problem that they have. When using a solution-focused approach, it is essential to help the coachee ‘reframe’ their ‘intractable’ problem into a more manageable one. Use the following questions:
- ‘So, how would you like the situation to be?’
- ‘What will it take to get what you want?’
- ‘What resources do you need?’
- ‘What resources do you already have?’
- ‘What two small steps could you take to help fix the situation?’
- ‘How far have you come already? Are there times when the solution is present, at least partly?’
Incorporating the ‘sparkling moments’ technique (see FWB2 Self-confidence and Self-efficacy Core Action 2.1) into peer coaching sessions can be highly effective. This can help us move towards a more positive mindset and identify both external and personal resources, such as our support networks and skills, which can help us reach solutions.
Peer coaching is a valuable tool for setting goals to improve overall well being, prioritise self-care, manage stress and enhance work-life balance. It is important to note, however, that while peer coaching can be beneficial, it is not a substitute for professional counselling. If a coach has deep-seated personal issues, seeking professional help is crucial. For more information on setting up a peer coaching relationship, see here.